-40%
Homo Neanderthal Anatomical Reconstruction skull in full real for archaeological
$ 59.78
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
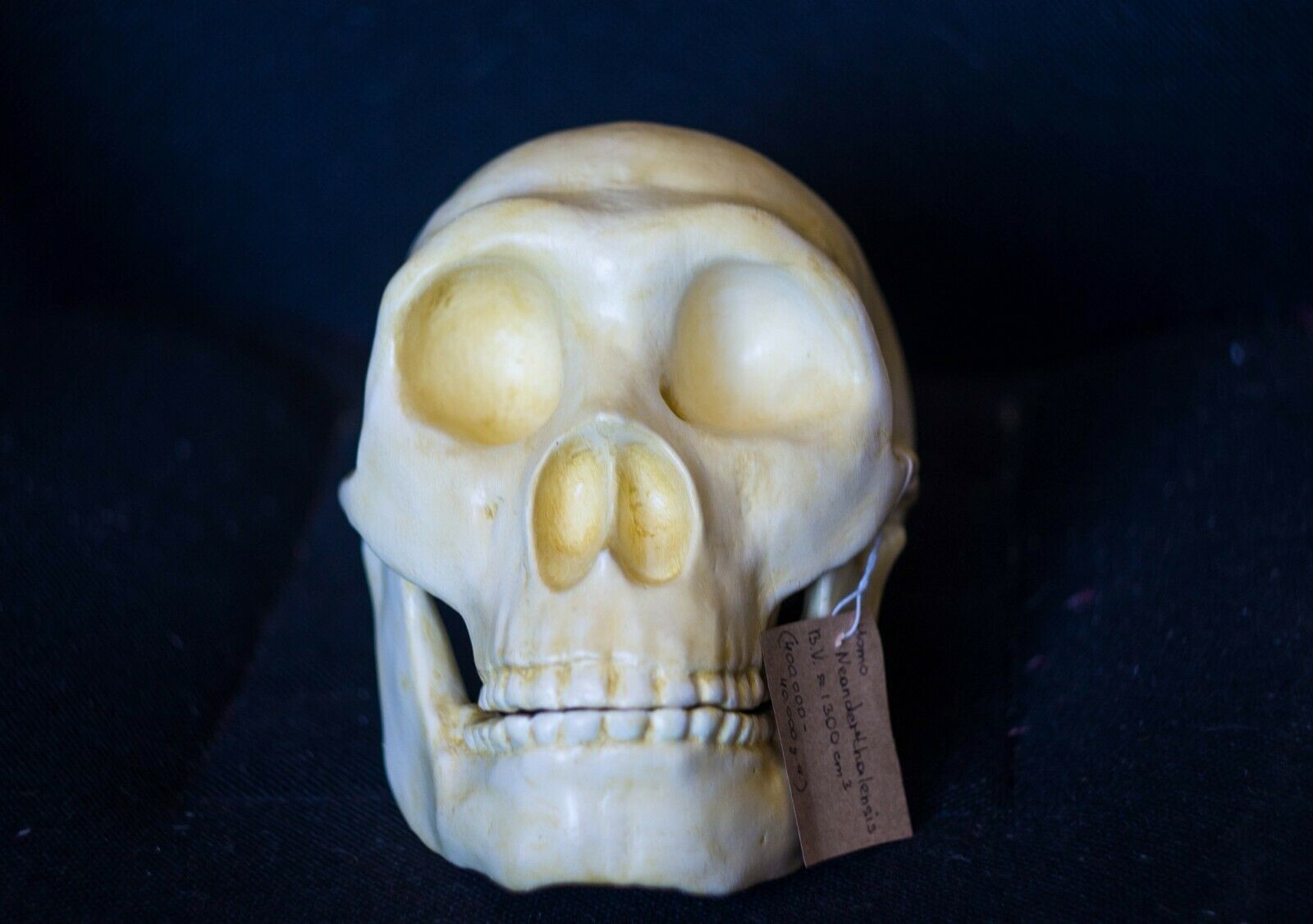
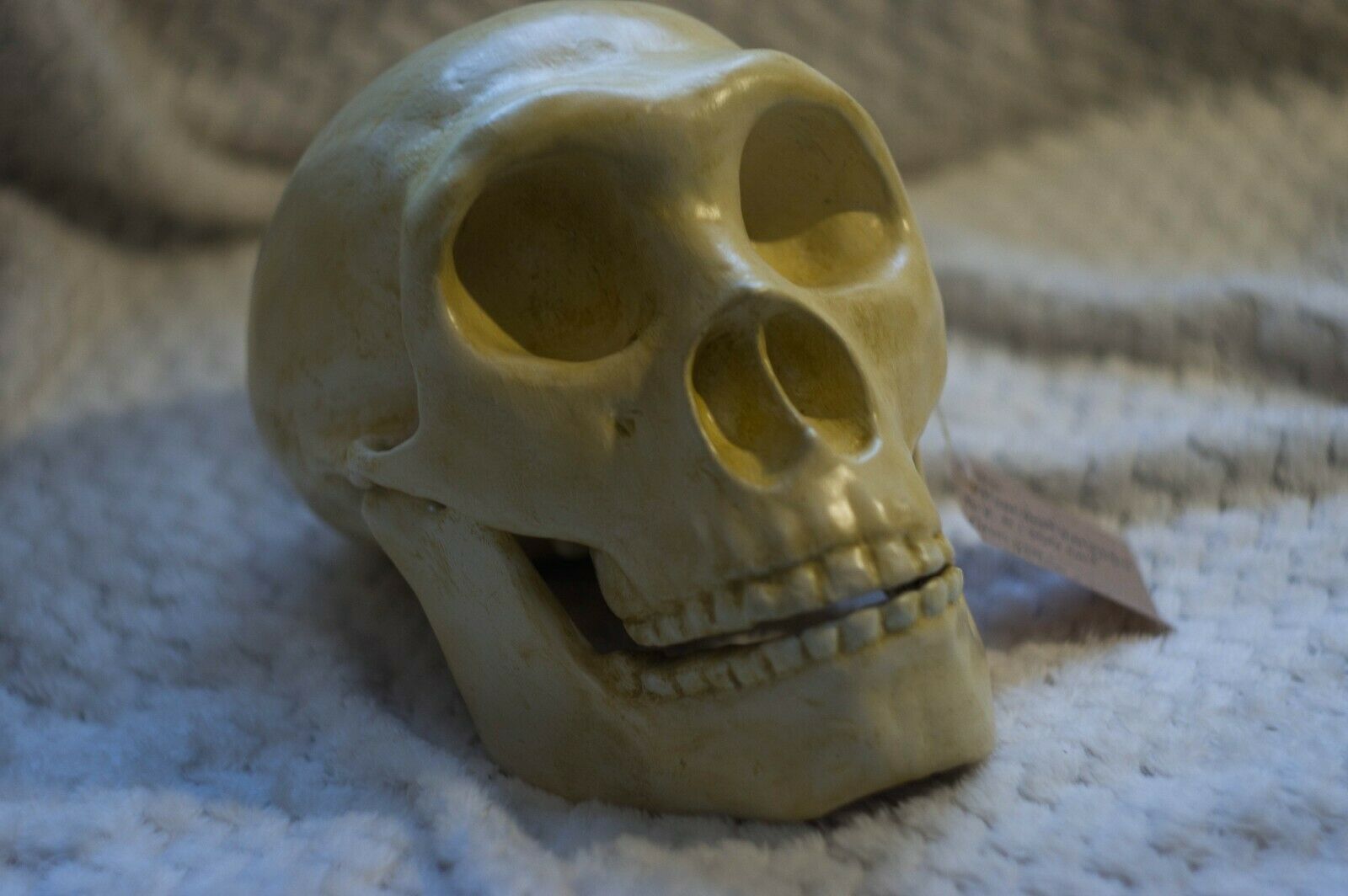
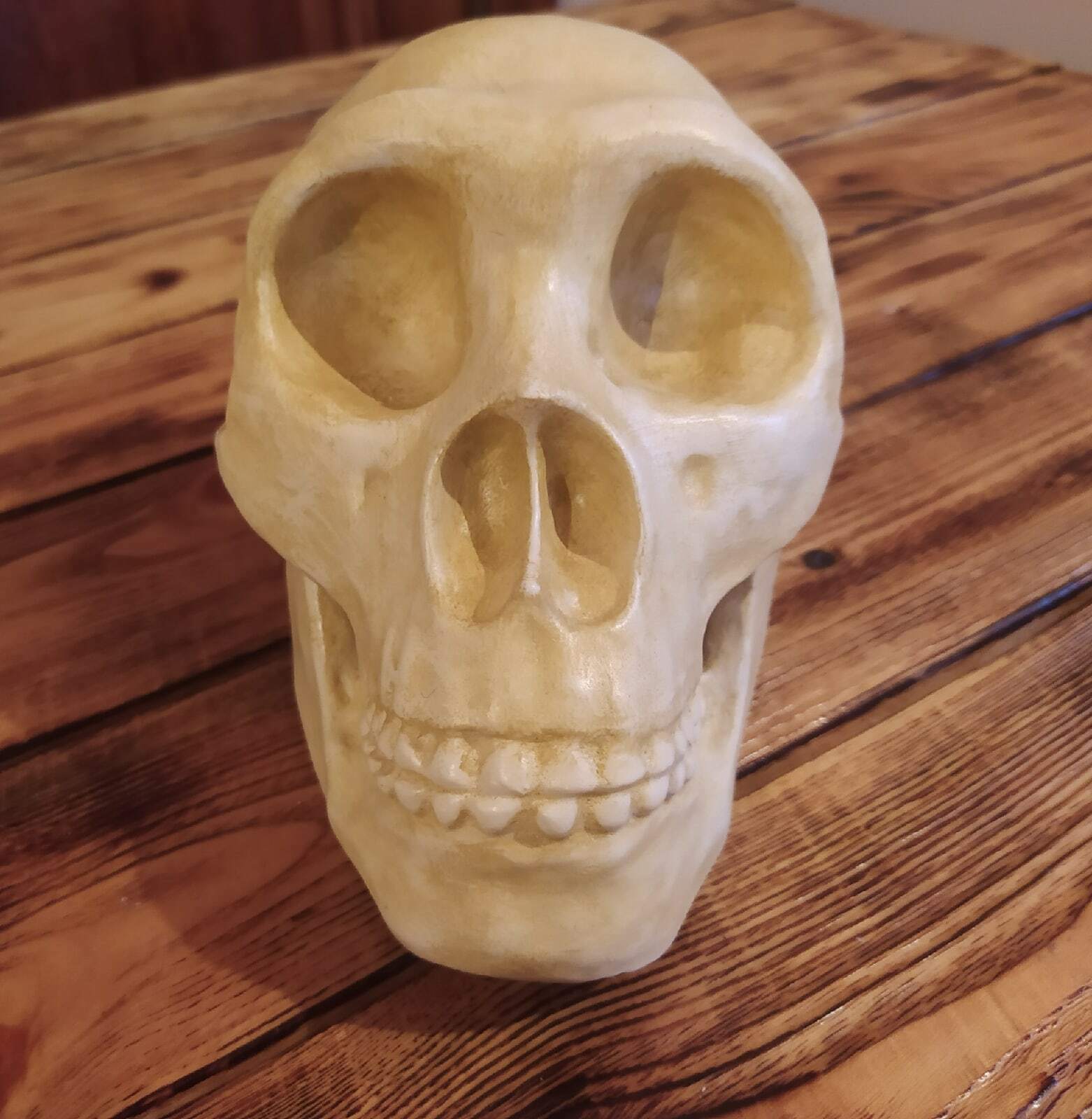
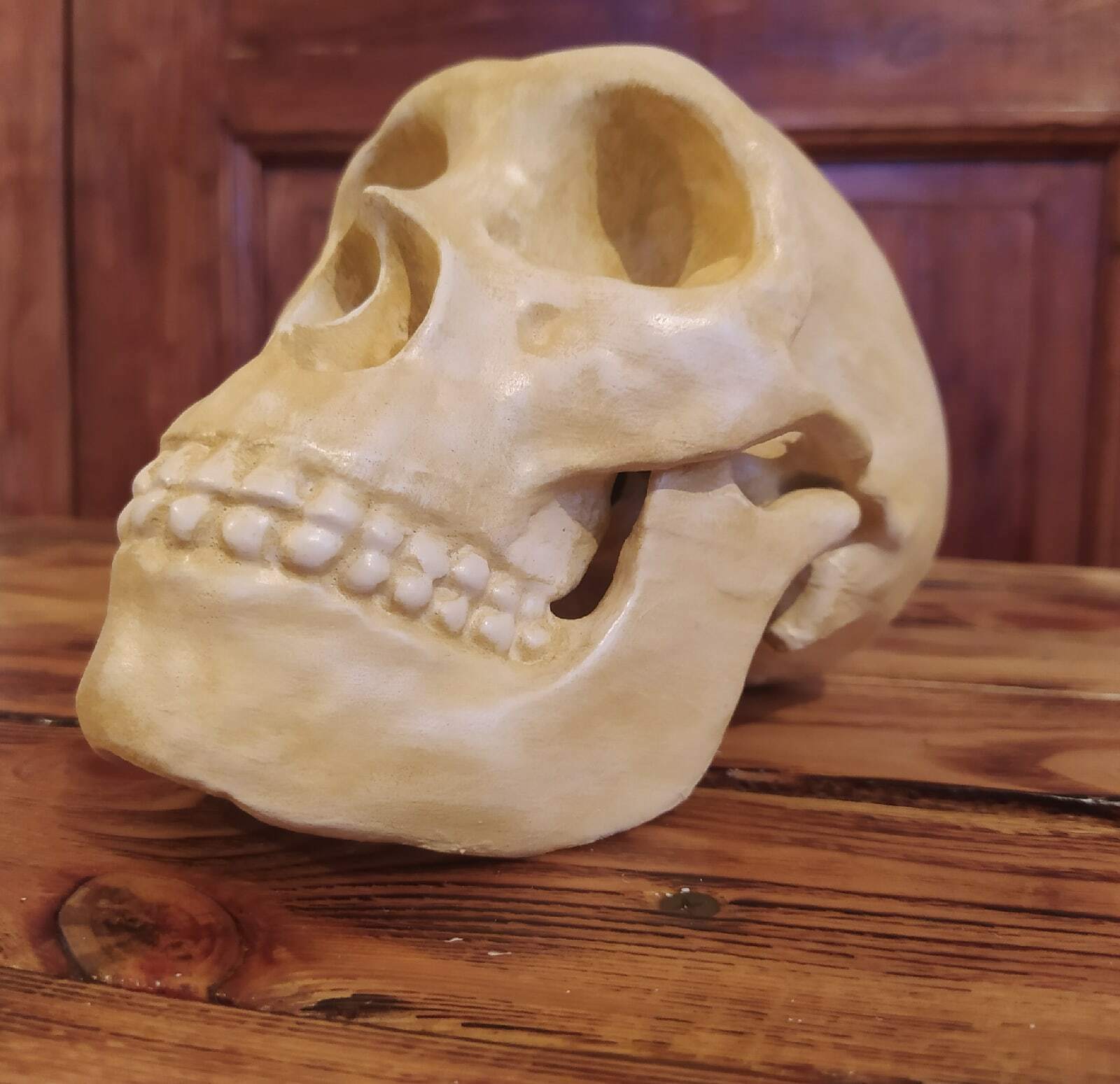
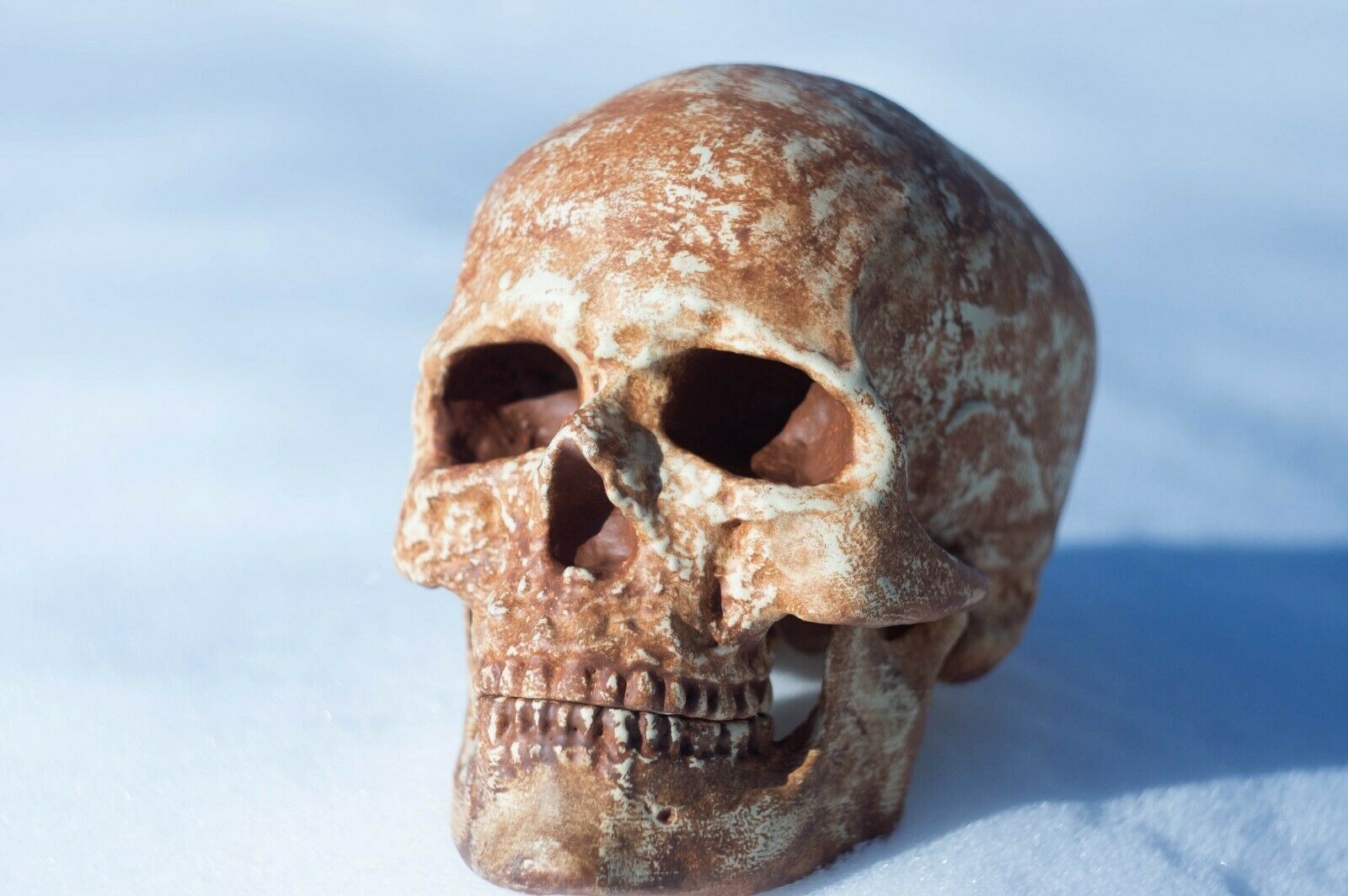
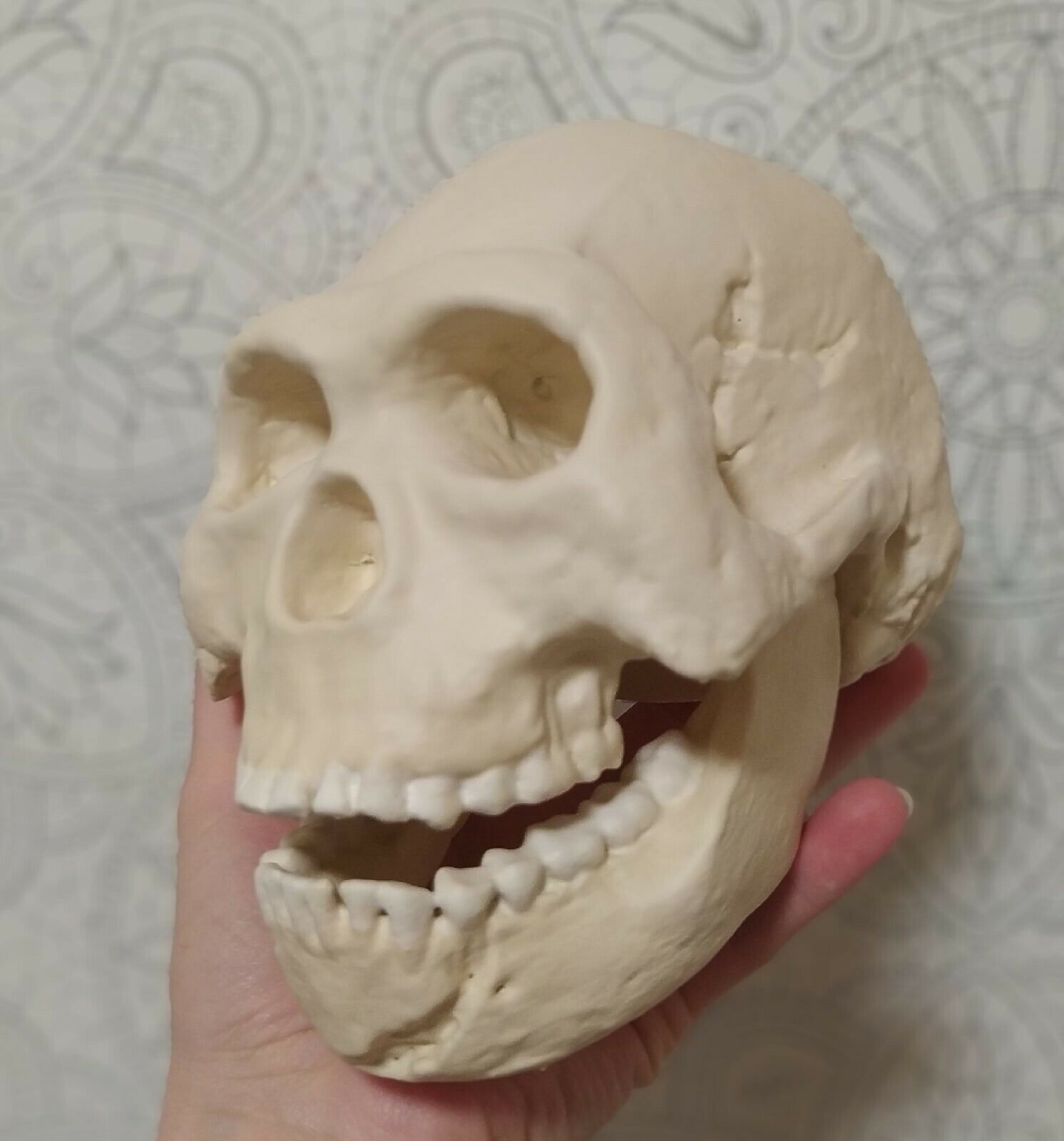
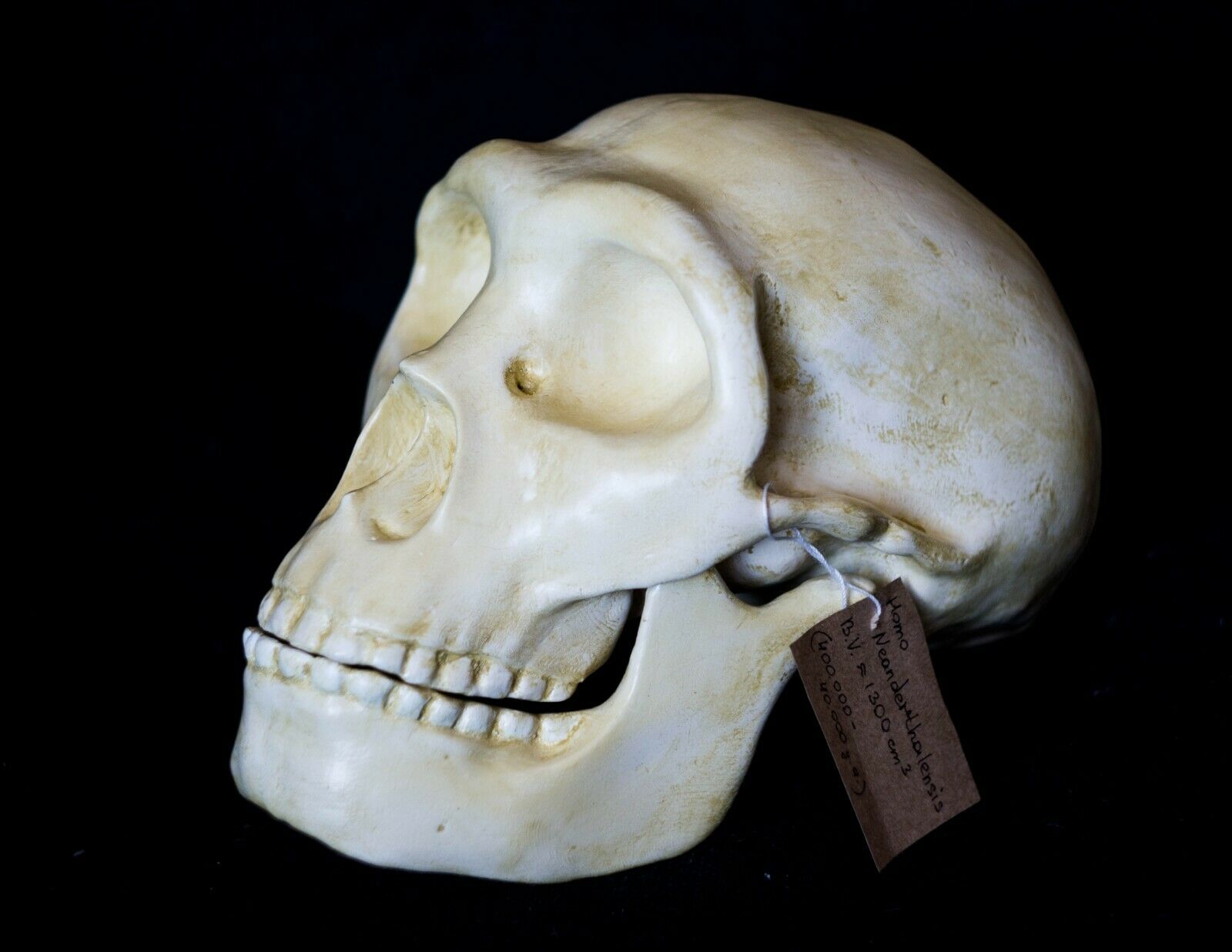
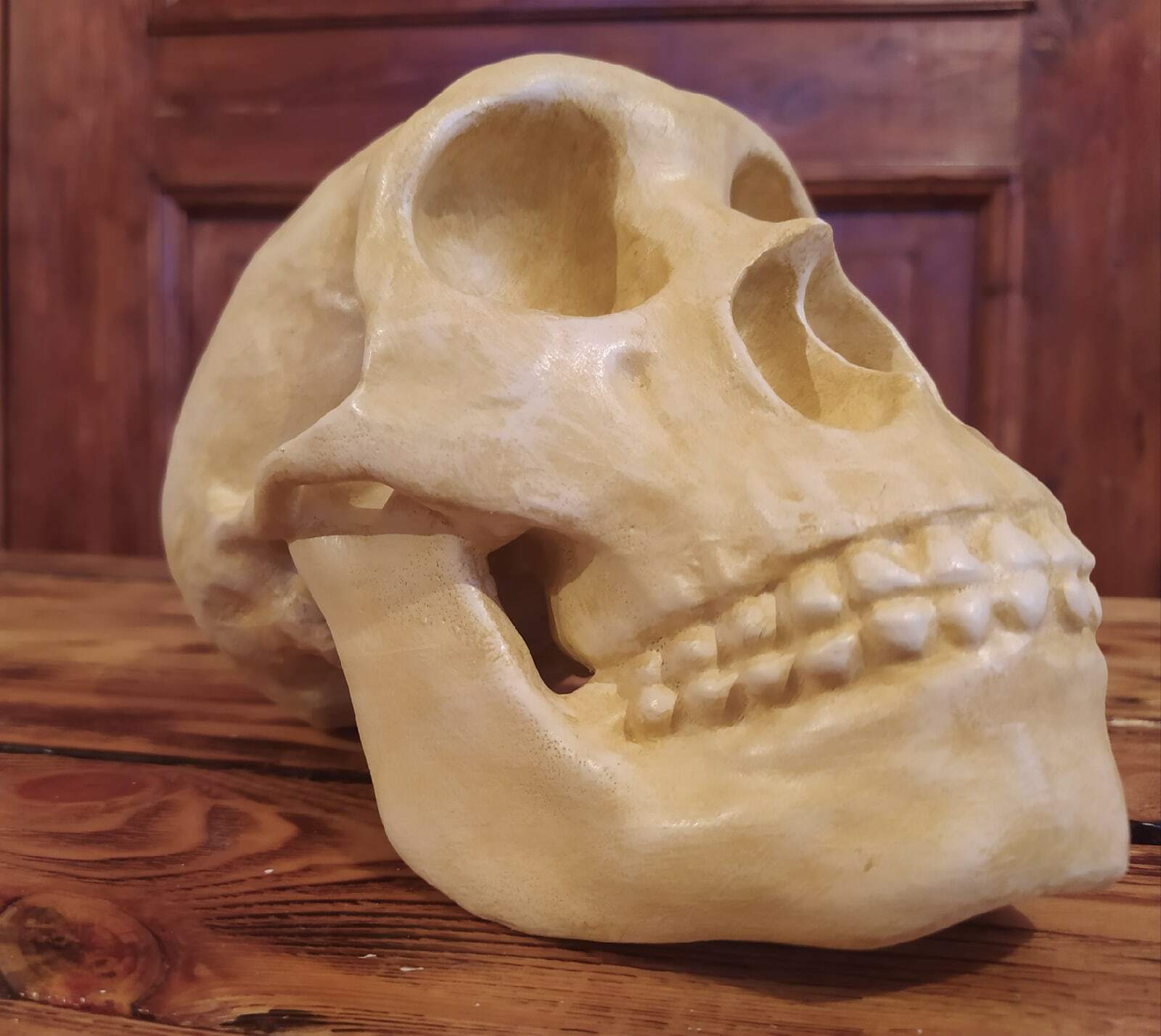
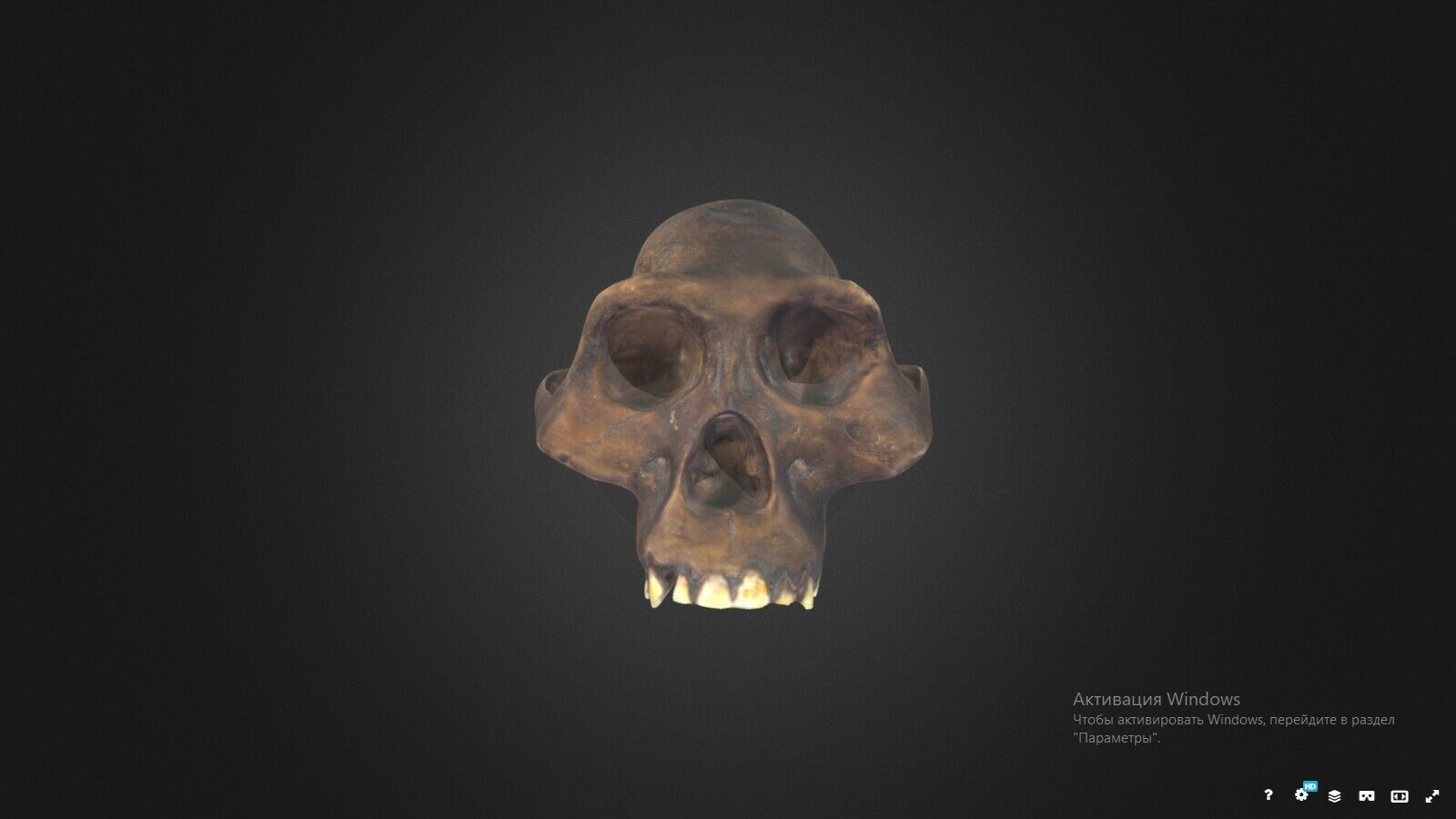
3D printed replica of a Neanderthal skull in full real size. Take the model for printing from the website of the Museum of Anatomy, which is engaged in the exhibition of anatomical models for 3d printing. This model of the skull was reconstructed taking into account all available data on the structure of the Neanderthal skull.Reconstruction of a Neanderthal skull found in the Spi cave, Belgium.
This version of the Neanderthal Homo skull is a pure reconstruction. It is more suitable for those who want a skull just for beauty. You can see more historical versions (scans from real fossils) of Neanderthal skulls in my profile.
Size: 21032mm
About this hominid:
Neanderthal or Neandertal is a relatively recent extinct member of the Homo genus that inhabited Europe and parts of western Asia in the middle to late Pleistocene, first appearing in the fossil record some 200,000 to 400,000 years ago and disappearing about 30,000 years ago. They are a sister group of present-day humans, with whom they came in contact during the later part of their history, from at least 80,000 years ago, and by whom they were displaced. They are variously classified as a species (Homo neanderthalensis) or subspecies (H. sapiens neanderthalensis).
Neanderthal brain sizes have been estimated to be larger than modern humans, although such estimates have not been adjusted for their more robust builds; their brain sizes are proportional to their more robust frame. Neanderthals also had a large cranial capacity, estimated at 1500cc, which is slightly larger on average than modern humans (1350 to 1450cc range).
Neanderthals also differed from modern humans in that they had a low forehead, double-arched brow ridge, larger nasal area, projecting cheek region, weak chin, obvious space behind the third molar, heavily-built bones, broad scapula, short lower leg and arm bones relative to the upper portions, occasional bowing of the limb bones, the hip joint rotated outward, a long and thin pubic bone, and large joint surfaces of the toes and long bones.